LeetCode: 99. Recover Binary Search Tree
The Problem
You are given the root of a binary search tree (BST), where the values of exactly two nodes of the tree were swapped by mistake. Recover the tree without changing its structure.
Example
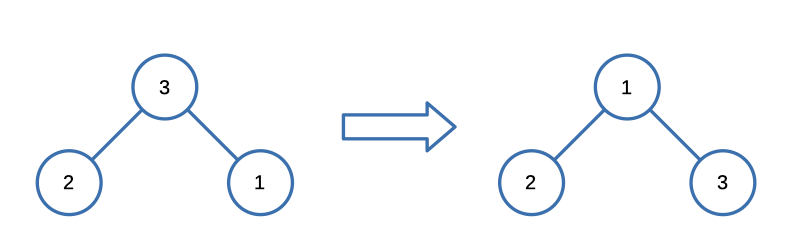
Input: [1,3,null,null,2]
Output: [3,1,null,null,2]
Explanation: 3 cannot be a left child of 1 because 3 > 1. Swapping 1 and 3 makes the BST valid.Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[2, 1000]. -231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
Solution
We opted for a recursive approach to tackle this problem, and upon evaluating our solution on the LeetCode platform, we achieved the following outcome:
Here's the code that led us to this result.
void recoverTree(TreeNode* root) {
TreeNode *prev = nullptr, *first = nullptr, *second = nullptr;
// Perform an in-order traversal to find the misplaced nodes
trasverse(root, prev, first, second);
swap(first->val, second->val);
}
void trasverse(
TreeNode* root, TreeNode*& prev, TreeNode *&first, TreeNode *&second
) {
if (root == NULL) return;
trasverse(root->left, prev, first, second);
if (prev && root->val < prev->val) {
if(first == NULL) first = prev;
second = root;
}
prev = root;
trasverse(root->right, prev, first, second);
}Here's a breakdown of how the code works:
1. void recoverTree(TreeNode* root): This is the main function that takes the root of the BST as input and is responsible for recovering the BST. It initializes three pointers: prev, first, and second. prev is used to keep track of the previous node visited during the in-order traversal, while first and second are used to store the two misplaced nodes.
2. trasverse(root, prev, first, second);: This line calls the trasverse function to perform an in-order traversal of the BST and identify the two misplaced nodes.
3. swap(first->val, second->val);: After the traversal is complete and the two misplaced nodes are identified, this line swaps the values of the first and second nodes to correct the BST.
4. void trasverse(TreeNode* root, TreeNode*& prev, TreeNode*& first, TreeNode*& second): This is a recursive helper function that performs an in-order traversal of the BST. It takes the current node root, a pointer to the previous node prev, and pointers to the first and second misplaced nodes.
- If the current node is
NULL, it returns, indicating the end of a branch. - It recursively traverses the left subtree by calling
trasverse(root->left, prev, first, second). - It checks if the
prevnode is notNULLand if the value of the current noderoot->valis less than the value of theprevnode's value. If this condition is met, it means the current node is misplaced. - If
firstisNULL, it assigns theprevnode tofirst, indicating the first misplaced node. Otherwise, it assigns the current noderoottosecond, indicating the second misplaced node. - The
prevpointer is then updated torootfor the next iteration. - Finally, it recursively traverses the right subtree by calling
trasverse(root->right, prev, first, second).
