LeetCode: 965. Univalued Binary Tree
The Problem
A binary tree is uni-valued if every node in the tree has the same value.
Given the root of a binary tree, return true if the given tree is uni-valued, or false otherwise.
Example
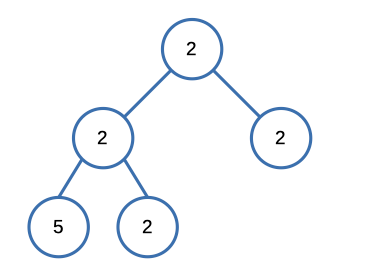
Input: [2,2,2,5,2]
Output: falseConstraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 100]. 0 <= Node.val < 100
Solution
We opted for a recursive approach to tackle this problem, and upon evaluating our solution on the LeetCode platform, we achieved the following outcome:
Here's the code that led us to this result.
bool isUnivalTree(TreeNode* root) {
return isUnivalTree(root, root->val);
}
bool isUnivalTree(TreeNode* root, int prev) {
if (root == nullptr) return true;
return prev == root->val &&
isUnivalTree(root->left, prev) &&
isUnivalTree(root->right, prev);
}🧠
Github with all the solution including test cases.
Let's break down the code step by step:
- The code defines a function
bool isUnivalTree(TreeNode* root)which takes a pointer to the root node of a binary tree as input and returns a boolean value (trueorfalse) indicating whether the tree is a univalued tree or not. - Now, let's look at the
isUnivalTreefunction with two parameters: This function takes two parameters:root, which is a pointer to a current node in the tree, andprev, which is the value of the parent node (or the value that is considered "uniform" for the current tree).
- The first line of the function checks whether the
rootnode is anullptr, which means it's an empty node. If it is, it returnstrue, as an empty tree is considered univalued. - The return statement is a bit more complex. It combines three conditions using the logical AND (
&&) operator:
prev == root->val: This checks if the current node's value is the same as the value of its parent. This is important because for a tree to be univalued, all nodes should have the same value.isUnivalTree(root->left, prev): This recursively checks if the left subtree is univalued with the same valueprev.isUnivalTree(root->right, prev): This recursively checks if the right subtree is univalued with the same valueprev.If all three conditions aretrue, then the function returnstrue, indicating that the tree rooted at the current node is a univalued tree. Otherwise, it returnsfalse.
