LeetCode: 653. Two Sum IV - Input is a BST
The Problem
Given the root of a binary search tree and an integer k, return trueif there exist two elements in the BST such that their sum is equal tok, orfalseotherwise.
Example
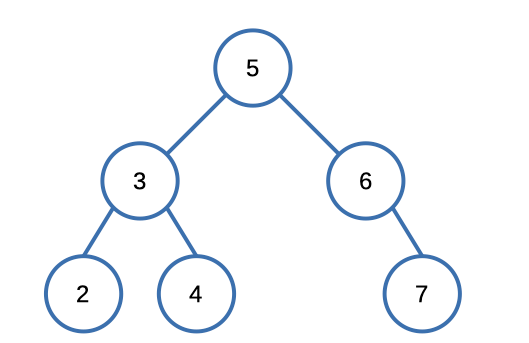
Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,7], k = 9
Output: trueSolution
We adopted a inorder recursive method to traverse the tree, while employing a two-pointer approach to resolve the problem. Upon assessing our solution on the LeetCode platform, the following outcome was achieved:
Here's the code that led us to this result.
bool findTarget(TreeNode* root, int k) {
vector<int> inOrderValues;
inOrder(root, inOrderValues);
int left = 0, right = inOrderValues.size() - 1;
while(left < right) {
int sum = inOrderValues[left] + inOrderValues[right];
if ( sum == k) return true;
(sum < k)? ++left : --right;
}
return false;
}
void inOrder(TreeNode *node, vector<int> &inOrderValues) {
if(node == NULL) return;
inOrder(node->left, inOrderValues);
inOrderValues.push_back(node->val);
inOrder(node->right, inOrderValues);
}🧠
Github with all the solution including test cases.
Explanation:
findTargetis a function that checks if there exist two values in a special type of tree (called a binary search tree) that add up to a given numberk.- We start by creating an empty list (vector) called
inOrderValues, which will store the values from the tree in an ascending order. - Then, we call the
inOrderfunction with the root of the tree and the empty vector. This function will help us traverse the tree and store its values in the vector while maintaining an ascending order. - After the
inOrderfunction is done, we'll have the values of the tree in an ascending order stored in theinOrderValuesvector. - We set up two pointers,
leftandright, initially pointing to the start and end of theinOrderValuesvector. - We use a
whileloop to compare the values pointed to byleftandright. If the value atleftplus the value atrightequals the targetk, we've found the two values that add up tok, so we returntrue. - If the sum of the values is less than
k, we increment theleftpointer to consider a larger value. - If the sum of the values is greater than
k, we decrement therightpointer to consider a smaller value. - If the pointers
leftandrightcross each other without finding a valid pair, we returnfalse. - The
inOrderfunction is a recursive function that helps us traverse the tree "in order" (from smallest to largest values). It visits each node and adds its value to theinOrderValuesvector. It does this by first visiting the left child, then the current node, and finally the right child.
