LeetCode: 199. Binary Tree Right Side View
The Problem
Given the root of a binary tree, imagine yourself standing on the right side of it, return the values of the nodes you can see ordered from top to bottom.
Example
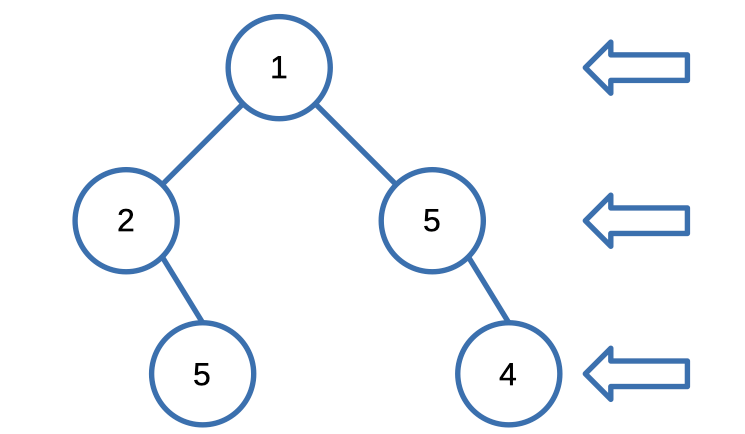
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,5,null,4]
Output: [1,3,4]Solution
We opted for a recursive approach to tackle this problem, and upon evaluating our solution on the LeetCode platform, we achieved the following outcome:
Here's the code that led us to this result.
vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> rightmost;
rightSideViewHelper( root, rightmost, 0);
return rightmost;
}
void rightSideViewHelper( TreeNode*& root, vector<int> &rightmost, int level) {
if (root == NULL) return;
int nextLevel = level + 1;
if(rightmost.size() < nextLevel) rightmost.resize(nextLevel);
rightmost[level] = root->val;
rightSideViewHelper( root->left, rightmost, nextLevel );
rightSideViewHelper( root->right, rightmost, nextLevel );
}The Main Function:
Here, rightSideView is like the main tour guide. It prepares an empty list called rightmost to store the people on the right side. Then it starts the tour by calling rightSideViewHelper from the root of the tree.
The Helper Function:
This helper function, rightSideViewHelper, is like your tour guide's assistant. It helps the main tour guide visit all the people in the tree.
- If there's no node at the current spot (if
rootis NULL), it means we reached the end of this branch of the tree, so we stop and go back. - We keep track of which level of the tree we're on. Think of levels as floors in a building.
- If the
rightmostlist isn't big enough to hold nodes at the next level, we make it bigger. - We meet a node (add their value to the
rightmostlist) if we haven't met anyone from their level on the right side yet. - Then, we continue the tour to the left and right, looking for more nodes.
